When a person has papilloma in mouth in any area, the first thing he feels is enormous discomfort. It is impossible not to detect a growth, since its appearance in the oral cavity is very clearly felt. To eliminate the discomfort with the first symptoms, you should consult a dermatologist, who will conduct diagnostic procedures and select the appropriate therapy.
Mouth papilloma is a mature benign neoplasm developing from surface epithelium cells. When viewed on the mucous membrane, single or multiple painless growths on the pedicles of a soft-elastic consistency of a pale pink or whitish color are determined. The general condition is not broken. The diagnosis of oral papilloma is made on the basis of complaints, anamnesis of the disease, clinical and histological data of research methods. Treatment of oral papillomas is surgical — a neoplasm is excised within healthy tissue. If viral etiology is detected, antiviral, immunomodulating therapy is prescribed. Check the key features of papilloma mouth and the best ways of their treatment.
![JIndianSocPedodPrevDent_2013_31_4_279_121833_f1[1]](https://papillomas.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/JIndianSocPedodPrevDent_2013_31_4_279_121833_f11-300x183.jpg)
Contents
- How Do Mouth Papillomas Differ from Other Growths?
- Is Mouth Papilloma a Benign Tumor?
- Why Do Papillomas Appear in Mouth?
- Classification of Oral Papillomas
- What Are the Symptoms of Mouth Papillomas?
- How to Diagnose Mouth Papillomas?
- What Is the Treatment of Mouth Papillomas?
- Stages of the Mouth Papilloma Removal
How Do Mouth Papillomas Differ from Other Growths?
The papilloma itself in the mouth is not considered a dangerous pathology, however, its growth over the entire cavity gives a constant discomfort. Although the growth is triggered by a viral agent, it does not cause serious painful symptoms, but is sometimes injured and bleeding. In such a situation, a favorable environment arises for bacteria to enter the patient’s body.
The proliferation of papilloma growths in the oral cavity is a rather serious cause for concern about the state of health. To reveal that the warts on the mucous membranes of the mouth are papillomas, it is possible by external manifestations, photos of which are on the Internet. Among them are: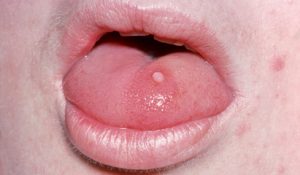
- sizes up to 10 mm;
- rough outer coating;
- rounded heads, with an expanded bottom, or a thin leg-thread for fastening;
- shade mucous light or pale pink;
- when you press on the growth of pain does not appear.
The reasons for the penetration of a viral agent into the body quite a lot. The greatest risk of infection through a liquid with the biological contents of a previously infected person, therefore, is at risk include those who:
- uses someone else’s brushes for cleaning teeth, washcloths or towels;
- does not wash hands with soap before eating;
- eats from dishes in public catering, which has not undergone sanitization;
- has unprotected sex.
Papilloma in mouth images can be viewed on various websites on the Internet, to have an idea of what papilloma growth looks like on the oral mucosa. Most of the patients infected with the papilomus agent do not know about it throughout their lives, if they did not pass special tests. An eruption on the gums and other parts of the mouth appears only in cases of changes in the hormonal background or a weakened immune system.
Papilloma in mouth pictures, papilloma growths may be similar to the formation of another types. Therefore, the diagnosis should be made by an experienced doctor. It is worth noting that the presence of even a number of factors cannot be a guarantee that the growths will affect parts of the mouth and other mucous membranes.
But in the above cases, a person should seriously engage in strengthening the immune system, rationing the mode of work with rest in order to minimize the chance of developing such diseases. Strengthened protective functions reduce the risk of spreading papillomas to almost zero rates.
Often, papilloma growths appear in the mouth of a baby. This happens because the kids practically taste all the objects of everyday life. They often do not follow hygienic rules and can become ill at the time of labor from the mother. Infection in the birth canal will cause the development of warts in infancy. They interfere with respiratory functions, causing the baby to cry incessantly.
Is Mouth Papilloma a Benign Tumor?
Oral papilloma is the most commonly diagnosed true benign tumor of stratified squamous epithelium. The main group of patients consists of women (60% of cases) at the age of about 40 years. In 20% of cases, oral papillomas are detected in adolescents. Among children, benign growths occur in the age group from 7 to 12 years. In girls, oral papillomas are diagnosed 1.9 times more often than in boys. In adults, in most cases, single papillomas are detected, whereas in children papillomatosis (multiple neoplasms) prevails. In 50% of the examined patients, oral papillomas are localized in the tongue. Human papillomavirus (6, 11 types) causes the formation of papillomas in 55-70% of cases.
Why Do Papillomas Appear in Mouth?
Benign tumors of the surface epithelium of the oral cavity in most cases result from exposure to human papillomavirus – HPV-6 and 11 types. Infection occurs through direct contact with the infected person. A neoplasm develops on the background of neutralizing the activity of tumor suppressor genes. Launching of the pathogenetic mechanism occurs after the HPV groups penetrate and infect the cells of the basal layer of the epithelium, as a result of which the regulatory processes of cell proliferation are disrupted.
Local predisposing factors are microdamages of the mucous membrane, the depth of which reaches the basal layer. For the development of the infectious process, the introduction of single virus particles is sufficient. The process of reproduction of daughter DNA molecules on the basis of the parent occurs exclusively in the basal layer of the integumentary epithelium. As a result of infection, the cell differentiation mechanism is disturbed. Since HPV is a weak antigen, the rate of synthesis of endogenous interferon is reduced. There is a deficiency of cellular immunity.
Multiple oral papillomas arise as a result of chronic damage to the mucous membrane by the sharp edges of the destroyed teeth, unpolished by the base of the denture. In children with a shortened frenulum of the tongue, oral papillomas are often diagnosed as a result of injury to the frenulum with the lower incisors.
Microscopically, oral papilloma is a tumor consisting of highly differentiated stratified squamous epithelium with signs of keratinization. The integrity of its own membrane, cell polarity, and complexity are preserved. The ratio of the structural components of the epithelium and stroma is disturbed. In some places, focal inflammatory infiltration may occur.
Classification of Oral Papillomas
In dentistry, there are single oral papillomas and multiple neoplasms — papillomatosis. Check the oral papilloma classification. By the nature of the etiological factor, oral papillomas are divided into 3 groups: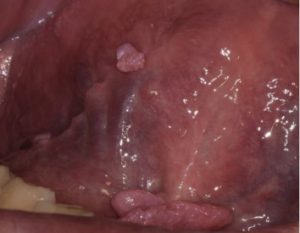
- Traumatic (reactive). It occurs as a result of exposure to mechanical, chemical or thermal stimuli. A distinctive feature of oral papillomas of reactive origin is the arrest of their growth after elimination of the causative factor.
- True (neoplastic). It develops due to violation of the mechanisms of control of division, growth, differentiation of cells. They are more often diagnosed in the distal parts of the cheeks, in the retromolar zone, closer to the pterygo-mandibular fold.
- It occurs as a result of infection with human papillomavirus. HPV infection occurs after contact with a sick person. At violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane, the gate opens for the introduction of viral particles.
What Are the Symptoms of Mouth Papillomas?
Papillomas of mouth are an overgrowth of a rounded mucous on a pedicle with a fine-grained, folded or warty surface. The base of the neoplasm is thin or wide. The mucous membrane around the base of the papilloma is pale pink in color, without visible pathological changes. On palpation, benign neoplasms of soft elastic consistency, painless. Mucous, covering the tumor, may have a pale pink or whitish tint, which is associated with keratinization of the epithelium as a result of maceration with saliva.
The sizes of papillomas vary from 0.2 to 2 cm. There are both single and multiple neoplasms. Favorite localization of oral papillomas are the tongue, hard and soft palate. Less commonly, a tumor is diagnosed in the area of the cheek, in the area of the floor of the mouth, or in the retromolar zone. Multiple oral papillomas are more often detected on the palate. After biting teeth, papilloma bleeds, as a result of injury acquires a dark color, due to hemorrhage into it.
Oral papillomas are characterized by a slow exophytic type of growth. The skin color is not changed. Opening mouth is free. Regional lymph nodes are not palpated. The general condition of the patients is the same. In the case of chronic injury on the surface of the papilloma appear areas of ulceration, which may signal the malignancy of the tumor.
How to Diagnose Mouth Papillomas?
Diagnosis of oral papilloma is based on the basis of patient complaints, anamnesis of the disease, clinical examination data. Accurate confirmation of the diagnosis can be obtained after the histological examination. On physical examination, the dentist detects growth in the form of a nodule of a roundish whitish or pale pink color without signs of an inflammatory process on the oral mucosa. Palpation of oral papilloma is painless, soft consistency. The general condition of the patients is not disturbed.
In case of viral etiology of oral papillomas, human papillomavirus 6, 11 types are detected using the method of DNA hybridization. PCR diagnostics can confirm the presence of human papillomavirus in the body, as well as determine its type and quantitative composition. The decisive for the final diagnosis are the results of histological examination of the material obtained during surgery. When oral papillomas in the epithelium, cell polarity, stratification, and the integrity of its own membrane are preserved. Cellular atypism is mild.
Along with the proliferation of the spinous layer of the epithelium, hyperkeratosis is present in combination with acanthosis. Hyperplasia of the basal layer is observed. Mitotic activity increases. In the connective tissue the number of capillaries increases.
It is necessary to differentiate papillomas of the oral cavity from fibroma, Serra glands, warts, and hyperplasia of the mucous membrane as a result of somatic pathology. The examination is carried out by a dentist-surgeon. In identifying signs of malignancy, additional counseling by an oncologist is necessary.
What Is the Treatment of Mouth Papillomas?
Papilloma in mouth treatment can only be carried out by a qualified specialist after a thorough examination. Surgery is often used as the method of mouth pailloma treatment. Papilloma is operatively excised within the healthy tissue. The methods of electrocoagulation, cryosurgery, and sclerotherapy are rarely used, since after performing them it is impossible to conduct a histological examination of the material removed. In case of multiple papillomatous tumors, a combined technique is used: excision with a scalpel of the largest number of papillomas grouped, removal of single tumors is performed by electrocoagulation.
In case of oral papilloma of viral etiology, along with surgical treatment, antiviral and immunomodulating therapies are prescribed. The drug based on inosine, a synthetic derivative of purines, has pronounced antiviral and immunostimulating effects. As a result of the high mitotic activity of true oral papilloma after surgical treatment, the risk of tumor recurrence is high. If a neoplasm has arisen due to traumatizing the mucous membrane, the elimination of local irritating factors reduces the probability of subsequent relapses to zero.
It will be possible to eliminate a benign papilloma in mouth only after conducting a balanced complex therapeutic course. Pay attention only to the external manifestations of the infection is fundamentally wrong. Papilloma disappears, then appear in the same place after a short time period. Treatment can only begin after an examination by a doctor. You can begin treatment only after an examination by a doctor.
Relapses occur because the viral organism cannot be eliminated. Before treatment, the patient must pass certain tests and be diagnosed. The therapeutic complex of the doctor include:
- medical compositions for the treatment of oral cavity;
- surgical procedures;
- immunomodulators and other ways to strengthen the immune system.
Stages of the Mouth Papilloma Removal
At the 1st stage, the performance is completely dependent on the responsibility of the patient himself. It is important to recognize that the oral cavity is the gateway for microorganisms to penetrate all organs. In this regard, it is necessary to carefully monitor oral hygiene. The patient should consult a dentist in order to correct all dental problems. At home, mouth care should be strengthened and increased several times. Teeth brushing is carried out in conjunction with the rehabilitation of the tongue pillow and rinsing. All hygiene procedures should end with the application of a special ointment.
At the 2d stage, the squamous papilloma mouth is removed by surgical methods. This therapy is necessary if the patient is diagnosed with abundant growth of warts. In other cases, it will be sufficient to regularly use the prescribed drugs and antiviral drugs. If the papilloma has grown too large, then doctors can offer several options for its elimination in the hospital.
Surgical removal of papilloma is necessary if the patient is diagnosed with abundant growth of warts. Due to the increased moisture in the mucous membranes of the mouth, cauterize the warts with liquid nitrogen is not rational. Chemical interaction can occur and papilloma is transformed into a malignant tumor. For the mucous membranes of the mouth most often used a conservative excision, during which the growth is cut and applied cosmetic seam.
Coagulation is also an effective method. This is the process of cutting growth with the help of light waves. For the procedure can be applied laser or discharge of electric current. The choice of device usually depends on the arsenal of the medical institution. From the aesthetic side, preference is given to a laser machine.
At the last therapeutic stage, it is necessary to suppress the spread of the virus in the circulatory system. The doctor prescribes a complex of drugs to the patient, which block the activity of the infectious agent. The patient should follow all the prescriptions of the specialist to avoid the appearance of new papillomas within a month. Recommended vitamin complexes and a healthy diet. The body and the nervous system should not be subjected to stressful situations and shocks, as they can provoke a repetition of the disease.
Doctors allow the use of various popular recipes, which should not irritate the mouth or cause an allergic reaction. Home methods are used not only with the permission of the doctor, but after receiving all the results of a full examination. Experts note that in cases where the therapeutic course did not give positive results, you need to look for additional reasons for the appearance of growths. A viral agent can become not active under the influence of strong drugs, but after the expiration of their action, they can again provoke growths in the mouth and on other mucous membranes. Timely visit to the doctor will allow you to cope with the pathology in a short time without much difficulty.