Papillomavirus has many variations. The first Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) was isolated in 1964, and currently 74 types of these viruses are already known. Not all of them are dangerous to people. The following types of papillomaviruses cause disease: 6 and 11 type — genital warts that are located on the genital organs of men and women; 8, 11, 16, 18, 31, 35 — genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis; 6, 8, 11, 16 — molluscum contagiosum; 16 and 18 — can cause cervical and vaginal cancer (in women), penile and prostate cancer (in men). Find out whether it is possible to protect yourself from cancer caused by papilloma.
![image[1]](https://papillomas.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/image1-300x183.jpg)
Contents
- Who Is Under Risk of Having a Malignant Papilloma?
- What Factors May Trigger Turning a Benign Papilloma into Malignant?
- How Do Papillomas Become Malignant in Women Causing Cervical Cancer?
- How to Understand that Your Papilloma Has Become Malignant?
- What Stages Does a Benign Papilloma Pass to Become Malignant?
- Remove Papillomas Before They Become Malignant
Who Is Under Risk of Having a Malignant Papilloma?
HPV is a risk factor for cancer: First of all — cervical cancer, as well as external genital organs: the vulva in women, the glans in men. Fortunately, the presence of papillomavirus in the body does not mean that a person will have cancer for 100%. The presence of papillomavirus in the body does not mean that cancer will occur immediately. Between the time of infection and the formation of papilloma malignant takes at least 15 years. According to statistics, only 1 of the 3 carriers of the papillomavirus really gets sick. And in order for the presence of papillomavirus in the body to trigger the appearance of a malignant tumor, a person should have the reduced anti-cancer protection.
This includes the overcrowding of the body with free radicals, that is, molecules that have a damaging effect on the DNA of the cell. What increases the number of free radicals? Smoking, work in a stuffy room, lack of sunlight — for example, a person works 12 hours in the office and does not see the sun. Also, anti-cancer protection can be reduced by metabolic diseases (diabetes, obesity, some hormonal diseases), coffee, beer, chips and chocolate instead of good nutrition.
What Factors May Trigger Turning a Benign Papilloma into Malignant?
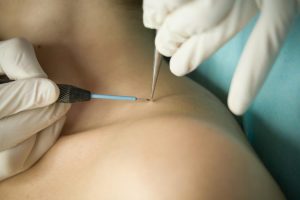
 Changes in the papiloma may be triggered if a person has one of the listed sexually transmitted infections: cytomegalovirus, genital herpes, chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis. Also, a banal inaccuracy can become a risk factor. Papillomas in the armpit, on the neck and face are often injured, after which they bleed and may become inflamed. Frequent injury of papilloma can contribute to its transformation into an inverted papilloma malignant. If you have large papillomas on your body that you often touch, you should consult the doctor concerning their removal.
Changes in the papiloma may be triggered if a person has one of the listed sexually transmitted infections: cytomegalovirus, genital herpes, chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis. Also, a banal inaccuracy can become a risk factor. Papillomas in the armpit, on the neck and face are often injured, after which they bleed and may become inflamed. Frequent injury of papilloma can contribute to its transformation into an inverted papilloma malignant. If you have large papillomas on your body that you often touch, you should consult the doctor concerning their removal.
So, it is possible to outline the following factors, which may become the cause of malignant papilloma process. The process of transformation of the growth into a cancer tumor occurs under the influence of adverse living conditions:
- unsuccessful attempts at self-removal of the wart;
- accidental damage to papilloma (rubbing against clothing, jewelry);
- sunburns of the skin;
- exposure to the infected area of the epidermis of ultraviolet rays;
- getting into the wart pathogenic microflora;
- improper removal of growth in beauty salons.
There are a number of circumstances in which the risk of degeneration of a wart into cancer increases significantly:
- chronic diseases of internal organs;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- drug addiction;
- overweight.
The wrong lifestyle in combination with various adverse factors increases the chances of turning any, even the most imperceptible growth into cancer. However, this does not mean that a person who does not have bad habits, should not be afraid of the appearance of cancer. The transition of a benign neoplasm to a malignant tumor cannot be controlled. Therefore, it is very important to diagnose papillomavirus at an early stage and consult a doctor promptly.
How Do Papillomas Become Malignant in Women Causing Cervical Cancer?
The link between HPV and cervical cancer is no longer doubtful: in 99.7% of cases of cervical cancer in patients, one of the HPV types is found. Two types of HPV are the most dangerous: 16 and 18 types provoke 70% of cases of cervical cancer and precancerous lesions. Cervical cancer develops only when the virus manages to stay in the body for a long time. In healthy women, the virus will require 15–20 years in the body to develop cervical cancer. The process can proceed faster (in 5–10 years) in women with impaired immune systems. Speaking about the risk group with such disorders, we mean, for example, HIV-infected women, and not patients with a so-called weakened immune system.
From the state of the norm to cancer, there must be several stages that can be treated. Intermediate stages are called dysplasia, or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. It is possible to detect these changes during cytological examination. In case of detection of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and HPV, treatment is recommended, which is a procedure for removing the affected area — more often with a radiobender — followed by a histological examination. After successful treatment in 95% of cases, HPV is not detected, which is a kind of signal of a properly performed surgery.
How to Understand that Your Papilloma Has Become Malignant?
Any type of cancer on the skin begins to manifest itself at the site of growth. Subsequently, in the absence of the necessary treatment, the patient’s general state of health worsens. A cancerous tumor can develop very slowly and cannot be diagnosed independently. In contrast to internal oncology, the malignancy of papilloma is always accompanied by pronounced external symptoms. Deterioration in general health can occur only when it is no longer possible to cure cancer.

You may notice the following local symptoms: the papilloma has been damaged and it doesn’t heal for long, the papilloma has changed its color, become red, and you always feel discomfort, which may be manifested in itching of the affected skin area. Also, at the last stage, there may be even bleeding and the desquamation of the upper epidermal layers.
What Stages Does a Benign Papilloma Pass to Become Malignant?
The transformation of a normal papilloma into malignant consists of several stages:
- initial stage — the tumor develops inside the growth and can be easily removed with it;
- the first stage — cancer cells penetrate into the layers of the dermis by about 2 mm, and the growth increases in size up to 2 centimeters;
- the second stage — the tumor grows up to 3-4 centimeters, as well as penetrates into all the epidermal layers;
- the third stage (progressive) — oncology affects nearby lymph nodes;
- the last stage — a patient has cancer metastases in the bone tissue and nearby organs (brain, lungs, liver, etc.).
Between the initial and last stage can take from 3 months to several years. The life expectancy of a patient with oncology is affected by his state of health and body resistance. When diagnosing late-stage papilloma cancer, some patients can live for 2-3 years and only 50% of cancer patients step over a five-year period.
Remove Papillomas Before They Become Malignant
The question of the need to remove papillomas is decided unequivocally — it is necessary to get rid of them if they are located at places where there is a high risk of turning into malignant papillomas. The fact that they reach large sizes or are injured by underwear and clothing may lead to the formation of non-healing, easily bleeding wounds into which an infection can penetrate.
Removal can be performed by various methods: traditional surgery, chemical cautery, thermal or cryodestruction. The most modern and safe types of surgery are radio wave and laser. The impact on the surrounding healthy tissue with them is minimized. When removing warts and papillomas with these methods, scarring in their place is almost completely excluded. Skin healing after removal occurs within a few days. In parallel with the removal, antiviral therapy is required. It is a must to strengthen the immune system. Modern medicine has not yet learned how to kill viruses. But it is also important that the carrier of HPV is not lifelong. In addition, there is a small amount of means at the disposal of medicine, which allow removing some of the viruses from the body. The use of these remedies is completely combined with immunomodulatory therapy.
The amount of virus in the body is directly related to the state of the body’s immunity — the better the immunity, the smaller the virus. Therefore, the most promising way to reduce the concentration of HPV in the body is to strengthen the immune system. For this, a separate course of treatment is carried out, after which the person begins to feel much better. Finally, there are very effective drugs for local use — creams, gels, sprays, which increase local immunity and reduce the concentration of the virus in the affected tissues. If you have noticed the first signs of changes in papillomas, if they cause even minor discomfort, consult your doctor concerning their removal- don’t wait until the last stage when they become malignant and can’t be treated!